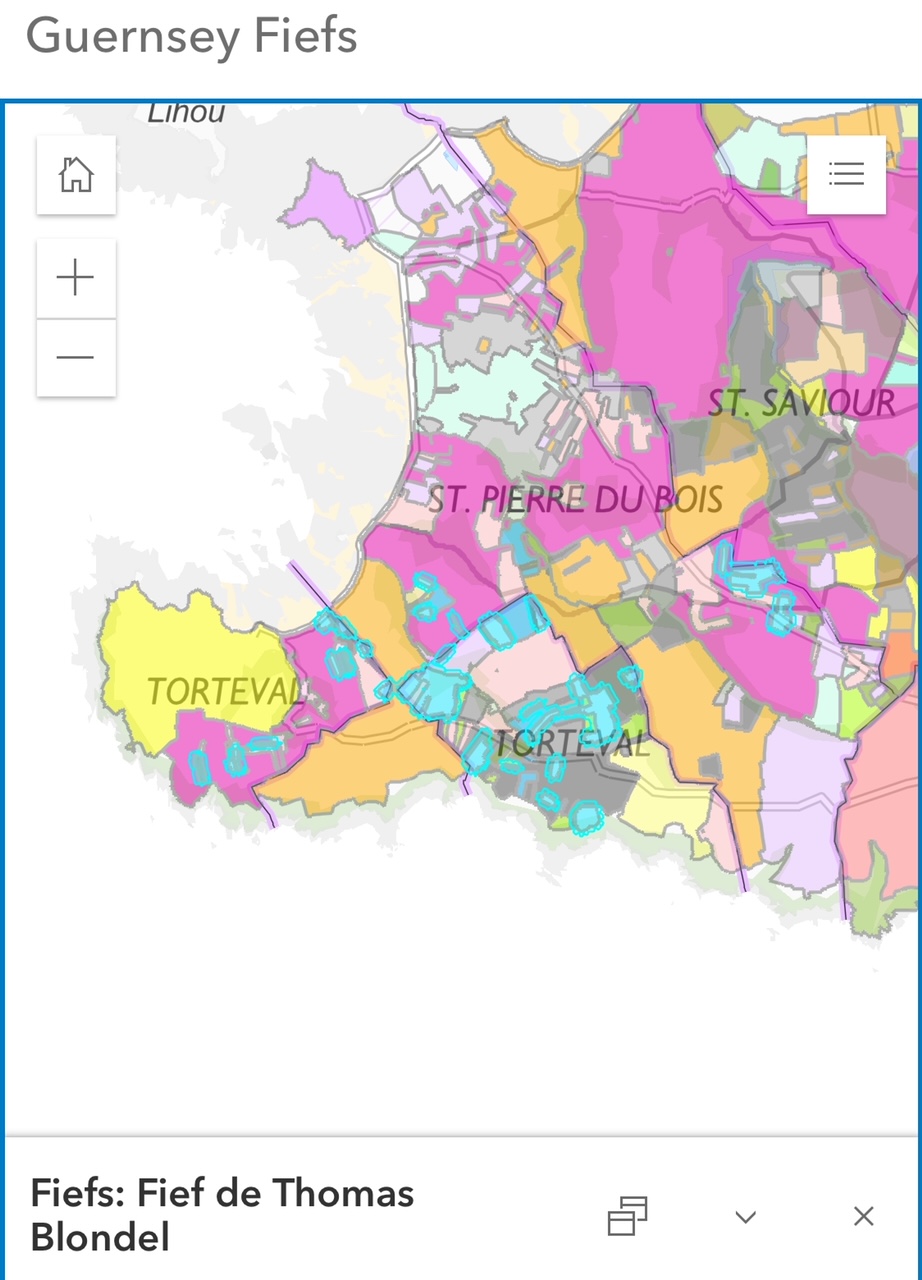
Fief Blondel Beaches Islands and Foreshore in Guernsey - UK Crown DependencyFief Thomas Blondel Est 1179 - Has Various Feudal Rights and Manorial Incidents related to its territory in St. Pierre du Bois and Torteval Parishes in Guernsey over the last 800 years of uninterrupted liberties, franchises, and rights as granted by the Kings and Queens of England. While the Seigneur of Sark has his own island, the Fief Thomas Blondel has 3 or more beachheads and foreshores on Guernsey. With these Beaches and Shorelines, The Fief Thomas Blondel and Seigneur claim the following:
** Note all humans, pets, boats, swimmers, and vessels are warned to stay away from any rocks or dangers in the bays. The Bissets Isles and The Hanois Isles have never been claimed except by the Foreshore Rights of the Fief Blondel. Lord Kinnear, in Smith v. Lerwick Harbour Trustees said about the Crown's property rights: "If the solum of Shetland as a whole is not originally the property of the Crown, I know of no authority, and can see no reason, for holding (saying) that part of it which is called the foreshore is Crown Property". This statement could equally well be applied to the seabed, especially since the foreshore is regarded as part of the seabed in English law. S.O.U.L. (udallaw.com) Today, there are 24 private lords totaling 46 lordships inherited from this feudal system , except that two of these 46 seigneuries are indivision between several owners. It appears that only 15 or so Private Fiefs own Beachfront, Foreshore and Maritime Rights. history of guernsey – Channel Islands (home.blog) Images from Old Postcards
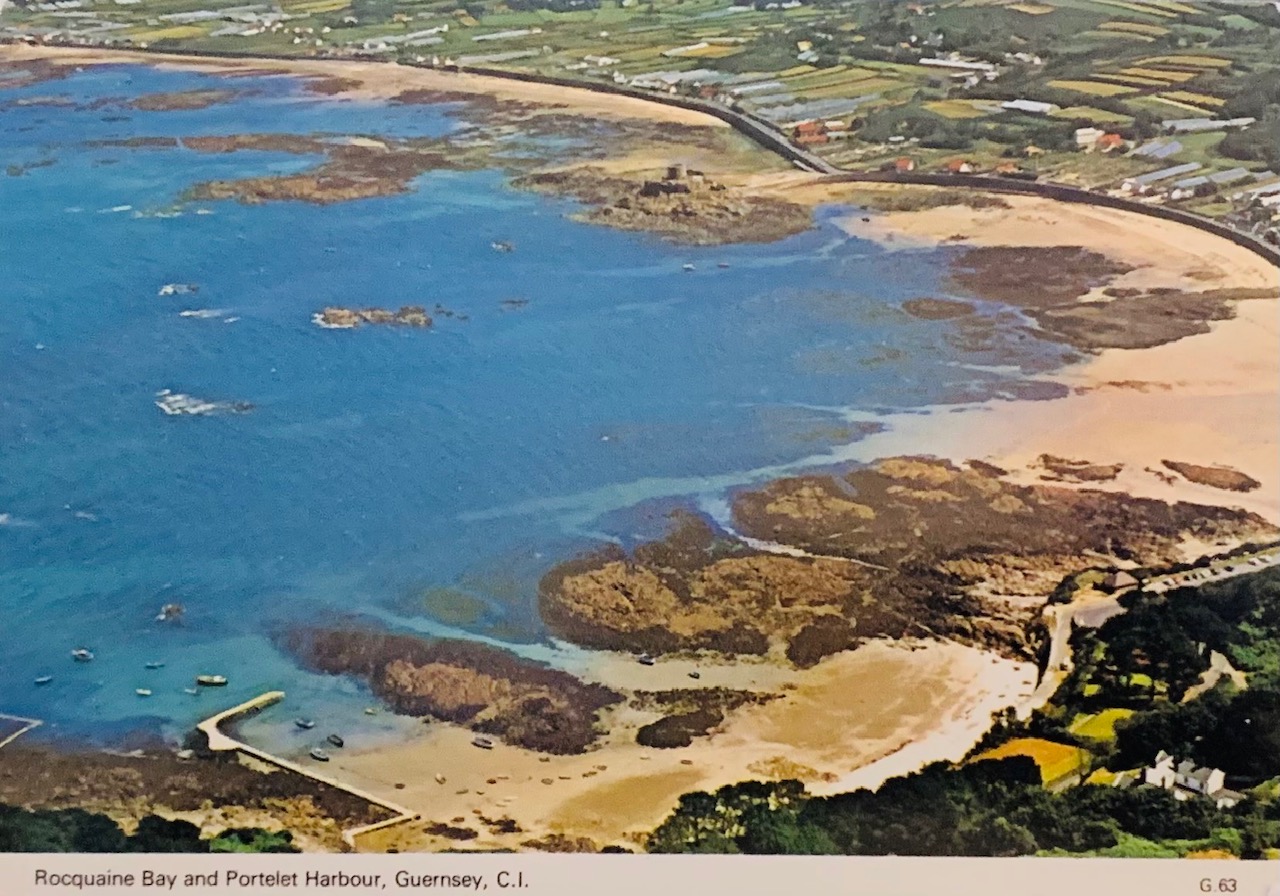
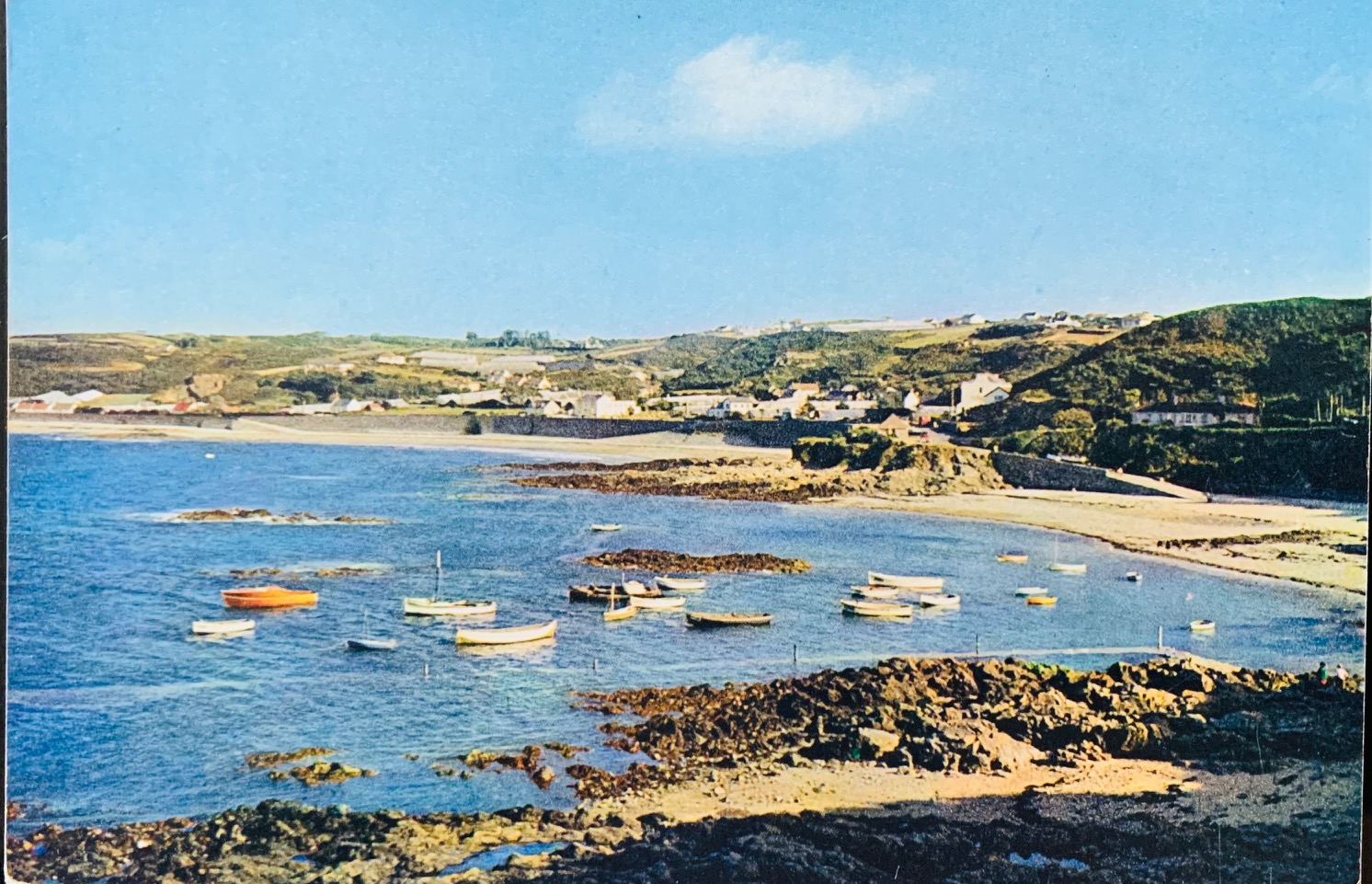
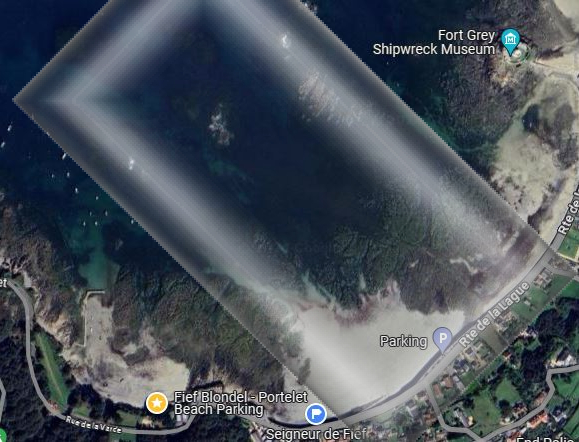
Images courtesy of Google Maps North Fief Blondel Beach - Portelet Bay
On either side of the Fief Thomas Blondel Territory, Beaches, Foreshores, territorial
waters, and Islands are the The Fief Pleinmont and Fief St. Michael which belong to the crown
for and the court, which consists of a seneschal, eleven vavasors, three prevosts, a greffier, and
serjeant, was held three times a year, viz. on the day following each of the Chief Pleas of the Royal Court,
at which the tenants are obliged to attend.
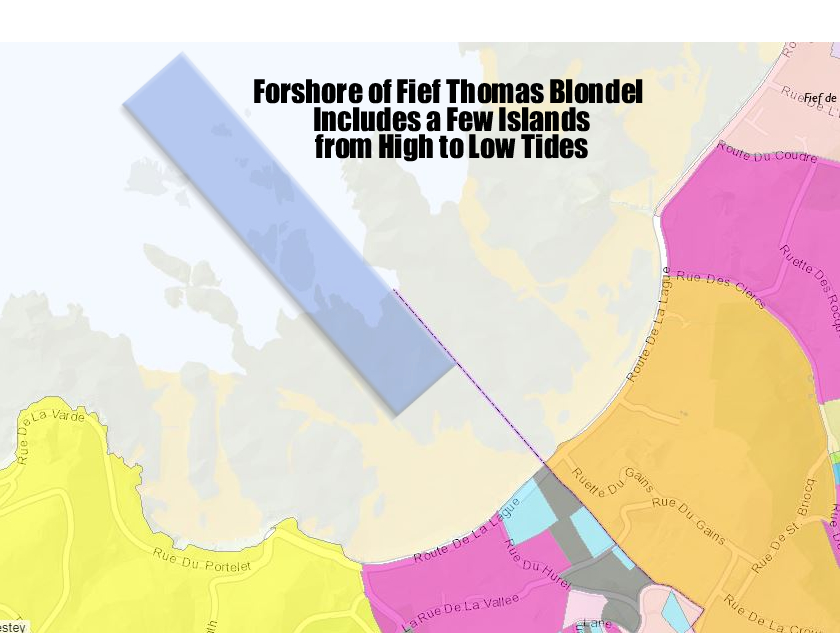
The Fief Blondel claims ownership and access and use rights to the island rocks of The Bissets and Les Hanoveaux or Hanois islands - The Fief Blondel officially warns the world and individuals to stay away from any and all reefs rocks and obstacles in their ships or boats or by swimming or diving.The Fief Blondel also claims international waters rights around such islands, reefs, and rocks coming above the water at any time from the shores of Fief Blondel.The Fief Blondel also claims rights to the styles of: The Prince and Viscount and Lords of the Bissets IslesThe Fief Blondel also claims rights to the styles of: The Prince and Viscount and Lords of The Hanois Isles The Fief Thomas Blondel claims part of the Les Bissets Islands off of the coast of Fief Blondel's Beach and Foreshore while also claiming partial rights to the Les Hanoveaux Islands.
Fief Blondel Islands on and with Foreshore
South Blondel Beach
Blondel Beach South Two Foreshore Rights under International Law and Crown Common Laws
* This page is designed to illustrate a Fief's rights to foreshore provided that the rules and laws in relation to foreshore are maintained in law.
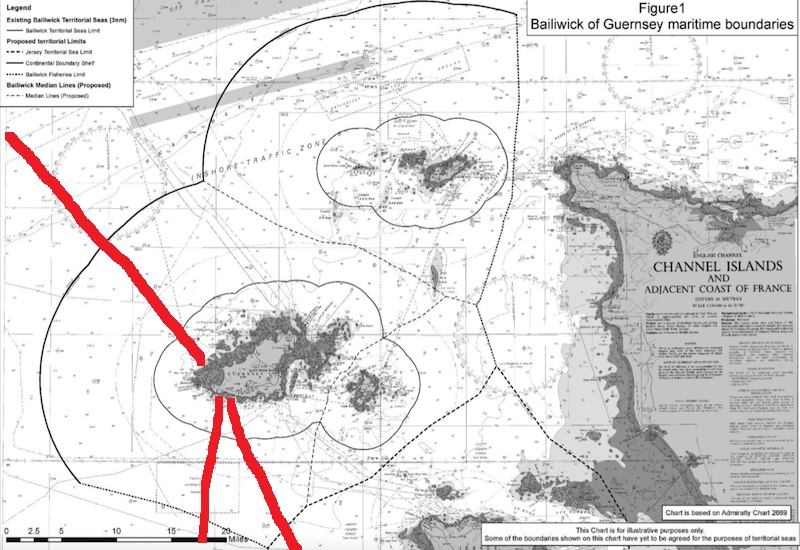
In the context of Jersey, a Crown dependency and self-governing territory of the British Crown, the ownership of the foreshore can indeed be unique due to its feudal legal system. The concept of the Lords Seigneurs owning the foreshore in Jersey is a specific legal arrangement derived from a thousand years of feudal law and customary law. In the case of Les Pas Holdings v Les Pas Farm Ltd. [2007] JLR 54, the Royal Court of Jersey considered a
dispute regarding the ownership of certain foreshore areas. The case involved a claim by the Seigneur of St. Ouen
that the foreshore in question belonged to the Fief of St. Ouen and was therefore part of his feudal rights as
Seigneur. It's important to note that Jersey's legal system is distinct from that of England and Wales, and it retains elements of customary law and feudalism. As such, the ownership of the foreshore in Jersey may differ from other jurisdictions. This case underscores the importance of understanding the unique legal framework of Jersey when considering questions of property rights, including those related to coastal areas and the foreshore. Historically, the Crown did have ownership over territorial waters around the Channel Islands, including Guernsey. Fishing rights have been owned by coastal Lords for over a 1000 years. The EEZ extends up to 200 nautical miles (approximately 370.4 kilometers). Marinas and Fishing requires water and rights to boating and to fish in the water. Coastal states have sovereign rights to explore and exploit natural resources on and beneath the seabed. The outer limit of the continental shelf can extend beyond 200 nautical miles if certain conditions are met. Monaco was historically a fief before it achieved sovereignty. The House of Grimaldi, a noble family from Genoa, Italy, gained control of Monaco in the late 13th century. The Grimaldis established themselves as rulers of the area and obtained sovereignty over Monaco, but initially, they did so as vassals of various larger powers. Monaco's status as a fiefdom meant that the rulers of Monaco owed allegiance to a more powerful lord or sovereign. Over the centuries, Monaco was at various times under the suzerainty of different entities, including the Holy Roman Empire, the Kingdom of France, and the Kingdom of Sardinia. However, in 1861, Monaco signed a treaty with France that established its full sovereignty, effectively ending its status as a fief. This treaty solidified Monaco's independence and recognized it as a sovereign state under the rule of the Grimaldi family. Since then, Monaco has maintained its sovereignty, although it has close ties with France, including agreements related to defense, currency, and other matters. Rocquaine Bay Regatta - Photo on Visit Guernsey Site Rocquaine Regatta | Visit Guernsey
La Grenouille or the Nipple Rock of Fief Blondel Guernsey (1000 Years of History ) The Islands and
Rocks are exposed as part of the high and low tides. Rocquaine Bay Link - Google Maps Link to Government Map of Guernsey showing islands and rocks and foreshores ADAS_Agricultural_Land_Classification.pdf (gov.gg)
|
Seigneur de la Fief of Blondel Lord Baron Mentz of Fief Blondel Geurnsey Crown Dependency Seigneur Fief of Blondel George Mentz Lord Baron of Fiefdom Blondel Freiherr of Fief Thomas Blondel Feudal Lord of Baronnie - Noble Fief Barony Friherre > Fief Blondel Islands Seigneurs and Dames Travel Research Lord Paramount Feudal Barons The Seigneur Order Patron George Mentz Charter of Liberties Deed & Title Fief Blondel Islands Viking Kingdom Fief Worship Fiefs of the Islands ECS Extended Continental Shelf Styles and Dignities Territorial Waters Blondel Privy Seal Fief Bouvees of Fief Thomas Blondel Guernsey Court of Chief Pleas Fief Court Arms Motto Flower Fief de l'Eperon La Genouinne Kingdom of West Francia Fief DuQuemin Bouvée Phlipot Pain Bouvée Torquetil Bouvée Bourgeon Bailiwick of Ennerdale Channel Island History Fief Direct from the Crown A Funny Think Happened On the Way to the Fief Guernsey Bailiwick of Guernsey - Crown Dependency Confederation des Iles Anglo-Normandes Sovereignty Papal Bull Research Links Norse Normandy Order of the Genet Order of the Genet Order of the Star Est. 1022 Knights of theThistle of Bourbon Count of Anjou Fief Rights Blondel and King Richard Press Carnival Manorial Incidents Appointments of Seigneurs Store Portelet Beach Roquaine Bay Neustrasia Columbier Dovecote Fief Blondel Merchandise Fief Blondel Beaches Islands Foreshore Events Fiefs For Sale Sold Lords of Normandy Fief Coin Viscounts de Contentin Fief Blondel Map Feudal Guernsey Titles Board of Trustees The Feudal System Hereditaments Chancellor Flag & Arms Fief Videos Guernsey Castle Sark Contact Advowson Site Map Disclaimer Freiherr Livres de perchage Lord Baron Longford Income Tax Guernsey Valliscaulian Order Saint Benedict of the Celestines Society of Divine Compassion Dictionary Count of Mortain Seigneur de Saint-Sauveur Seigneur of Fief Ansquetil Top Success Books Datuk Seri George Mentz Order St. Benedict OSB Celestines Order of the Iron Crown Order of the White Falcon Colonel Mentz Order Red Eagle Order St. Louis Order Holy Ghost Order of Saint Anthony Order of the Black Swan Order of St Columban Order of the Iron Helmet Livonian Brothers of the Sword Fief treizième and Direct from Crown Valuation Fief Blondel Prince of Annaly Teffia
Feudal Lord of the Fief Blondel of the Nordic Channel Islands Guernsey Est.
1179
Feudalherr - Fief Blondel von der Nordischen Insel Guernsey Est. 1179
New York Gazette - Magazine of Wall Street -
George Mentz -
George Mentz - Aspen Commission - Mentz Arms
Counselor George Mentz Esq. - Seigneur Feif BlondelBaron Annaly Baron Moyashel Grants to Delvin About Longford Styles and Dignities The Seigneur Court Barons Fiefs of the Islands Longford Map The Island Lords Market & Fair Fief Worship Channel Island History Fief Blondel Lord Baron Longford Fief Rights Fief Blondel Merchandise Events Blondel and King Richard Fief Coin Feudal Guernsey Titles The Feudal System Flag & Arms Castle Site Map Disclaimer Blondel Myth DictionaryMentz Scholarship Program 101 Million Donation - Order of the Genet Knighthood |





George Mentz Education -
Commissioner George Mentz
-
https://finance.yahoo.com/news/commissioner-george-mentz-clinches-influencer-180000705.html
-
George Mentz News -
George Mentz Net Worth - George Mentz Noble Tilte -
George Mentz -
George Mentz Trump Commissioner -
George Mentz Freiherren Count Baron -
George Mentz Global Economic Forum -
George Mentz Donates Millions